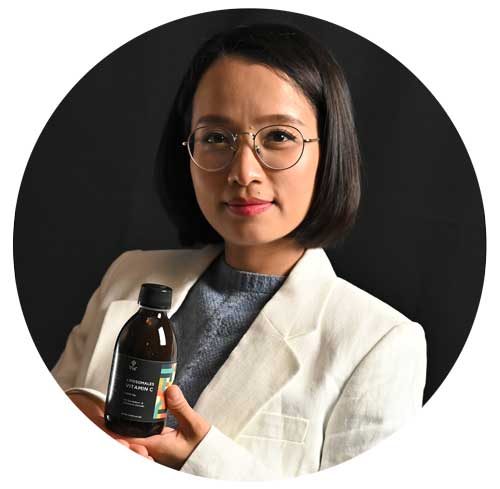
Atopic dermatitis, atopic eczema or neurodermatitis: These are all terms for the same skin disease, which occurs chronically or non-chronically again and again. It is usually characterized by dry, scaly skin that is very itchy. The skin changes are caused by a hereditary predisposition, which is why neurodermatitis is not a contagious skin disease. Since it is an atopic disease, like hay fever or asthma, it is also called atopic eczema. In the case of atopic diseases, the immune system reacts with a violent defense against substances in the environment that are actually harmless. These are the so-called allergens such as pollen or food. In this context, "atopic" means out of place, which expresses that the flare-ups of the disease can also occur in neurodermatitis without them being externally recognizable and appearing out of nowhere. It is one of the most common skin diseases . It often begins in childhood but also in infancy. At least temporarily, 10 to 15 percent of preschool children have neurodermatitis. It rarely occurs in adulthood. About 1.5 to 3 percent of adults in Germany have neurodermatitis. The frequency of neurodermatitis has increased significantly in recent years. In 1960 only every 30th child of preschool age was affected, today almost every 6th. The reason for the immense increase could possibly be the improvement in hygienic conditions and improved living conditions. In a clean environment, the immune system is less exposed to germs and may begin to react to harmless substances. City children, who come from better-off social classes, seem to suffer more frequently from atopic diseases such as atopic dermatitis, asthma or hay fever.

The reasons
These are not exactly known . However, it is clear that neurodermatitis is not contagious . Instead, the hereditary predisposition in particular is of great importance in the development of neurodermatitis. If atopic eczema occurs in twins, in the case of identical twins, both are affected in 75 percent. In the case of dizygotic twins, on the other hand, it is only 23 percent. If both parents suffer from neurodermatitis, the child will probably also develop this skin disease in 60 to 80 percent of cases. The cause of the characteristic skin inflammation that makes up neurodermatitis is an excessive defense reaction of the body to initially harmless substances such as house dust, pollen and food. These are the allergens. In this skin disease, certain white blood cells attack the allergens. The lymphocytes are responsible for fighting foreign and harmful substances. The body forms large amounts of defense substances, the antibodies, against these normally harmless allergens. The immunoglobulin E is a very important defense substance. In combination with various messenger substances from the immune system, the so-called cytokines, the IgE causes an inflammatory reaction of the skin's defences. Cytokines are among the building blocks of the immune system. With regard to pathogens, they control their defenses. The inflammatory reaction is fueled by various white blood cells, particularly T-lymphocytes. The body also releases histamine, an anti-inflammatory messenger. This further strengthens the immune response, which is the reason for the typical itching associated with neurodermatitis. The extent to which utopian eczema develops and whether it develops at all is determined immensely by environmental influences. The causes of a neurodermatitis flare-up include various allergens, mechanical skin irritations, certain foods, infections and also climatic conditions. In many cases, psychological stress also has an increased effect on neurodermatitis. Stress can also cause atopic eczema in a toddler. In each individual case, neurodermatitis has several causes of interacting environmental factors.
The symptoms
The typical symptoms primarily include skin problems. The skin is drier than normal skin and cannot store as much moisture. Furthermore, certain skin fats are missing in neurodermatitis of the skin. Because of this defect, it is very rough and flakes easily. In neurodermatitis, the skin also loses its function, which is important as a barrier against environmental substances. In addition, there is a disruption in the regulation of other skin functions, such as perspiration, blood circulation in the skin and temperature regulation. The skin and the environment are colonized with a large number of bacteria and none. People who have atopic eczema have an altered composition of these germs. This can intensify the neurodermatitis symptoms. The severity of the neurodermatitis symptoms says nothing about the degree of impairment. In individual cases, the signs can severely affect and burden those affected. Atopic eczema can therefore also reduce performance at school or at work and lead to difficulties in the social environment and also to depression. One of the most important symptoms in the neurodermatitis phase is itching. He occupies a central position. Scratching can make neurodermatitis worse. Treating the skin inflammation is particularly important to relieve or stop the itching. The symptoms change over the course of life. Three forms are distinguished based on age and body parts. In each of the phases, flare-ups can occur due to environmental influences or stress. Cradle cap, flexor eczema and prigoform are the three different forms.
The diagnosis

It is based on the anamnesis and a thorough physical examination. The doctor asks if relatives have the disease or if there are signs of an allergy. The parts of the body where the skin changes can be seen often provide clues as to whether it is neurodermatitis or not. Certain features of the body also appear more frequently and also contribute to the diagnosis, such as shadows under the eyes, deepened palm lines or a double crease on the edge of the eyelid. Skin tests and blood tests are also available.
The therapy
A two-component therapy is the right thing to do in this case. These are the basic therapy and treatment of skin inflammation. The basic therapy aims at moisturizing the skin and consists of regular skin care. Care preparations should be applied generously. Medicines can be taken to counteract the skin inflammation, depending on the course of the neurodermatitis and the affected areas. In the case of mild to moderate neurodermatitis, external treatment is usually sufficient to improve the symptoms and antihistamines, for example, can also be taken. In severe cases, internal therapy for neurodermatitis in the form of anti-inflammatory substances is also necessary.